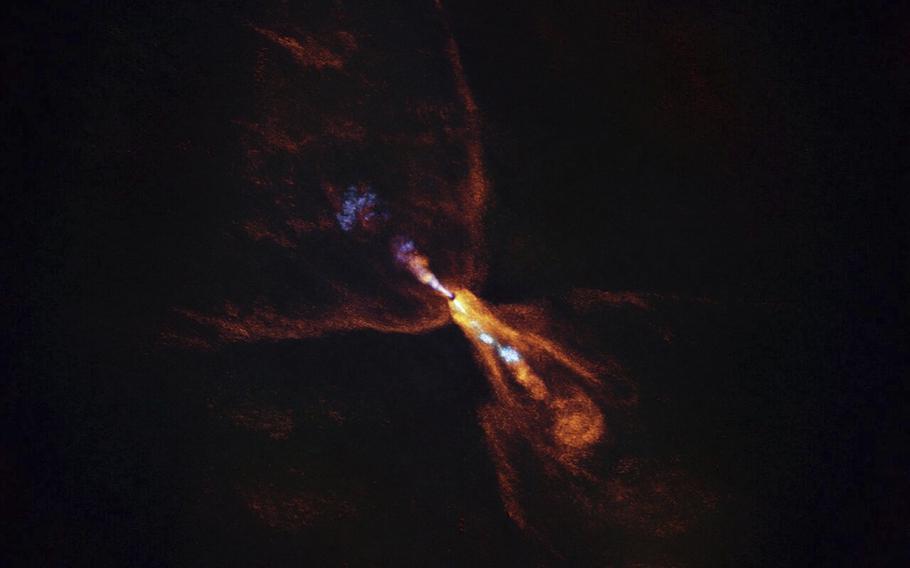
This image provided by the European Southern Observatory on Tuesday, July 15, 2025, shows HOPS-315, a baby star where astronomers have observed evidence for the earliest stages of planet formation. (ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), M. McClure et al. via AP)
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. — Astronomers have discovered the earliest seeds of rocky planets forming in the gas around a baby sun-like star, providing a precious peek into the dawn of our own solar system.
It’s an unprecedented snapshot of “time zero,” scientists reported Wednesday, when new worlds begin to gel.
“We’ve captured a direct glimpse of the hot region where rocky planets like Earth are born around young protostars,” said Leiden Observatory’s Melissa McClure from the Netherlands, who led the international research team. “For the first time, we can conclusively say that the first steps of planet formation are happening right now.”
The observations offer a unique glimpse into the inner workings of an emerging planetary system, said the University of Chicago’s Fred Ciesla, who was not involved in the study appearing in the journal Nature.
“This is one of the things we’ve been waiting for. Astronomers have been thinking about how planetary systems form for a long period of time,” Ciesla said. “There’s a rich opportunity here.”
NASA’s Webb Space Telescope and the European Southern Observatory in Chile teamed up to unveil these early nuggets of planetary formation around the young star known as HOPS-315. It’s a yellow dwarf in the making like the sun, yet much younger at 100,000 to 200,000 years old and some 1,370 light-years away. A single light-year is 6 trillion miles.
In a cosmic first, McClure and her team stared deep into the gas disk around the baby star and detected solid specks condensing — signs of early planet formation. A gap in the outer part of the disk gave allowed them to gaze inside, thanks to the way the star tilts toward Earth.
They detected silicon monoxide gas as well as crystalline silicate minerals, the ingredients for what’s believed to be the first solid materials to form in our solar system more than 4.5 billion years ago. The action is unfolding in a location comparable to the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter containing the leftover building blocks of our solar system’s planets.
The condensing of hot minerals was never detected before around other young stars, “so we didn’t know if it was a universal feature of planet formation or a weird feature of our solar system,” McClure said in an email. “Our study shows that it could be a common process during the earliest stage of planet formation.”
While other research has looked at younger gas disks and, more commonly, mature disks with potential planet wannabes, there’s been no specific evidence for the start of planet formation until now, McClure said.
In a stunning picture taken by the ESO’s Alma telescope network, the emerging planetary system resembles a lightning bug glowing against the black void.
It’s impossible to know how many planets might form around HOPS-315. With a gas disk as massive as the sun’s might have been, it could also wind up with eight planets a million or more years from now, according to McClure.
Purdue University’s Merel van ‘t Hoff, a co-author, is eager to find more budding planetary systems. By casting a wider net, astronomers can look for similarities and determine which processes might be crucial to forming Earth-like worlds.
“Are there Earth-like planets out there or are we like so special that we might not expect it to occur very often?”
AP video journalist Javier Arciga contributed to this report.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.